There is a good reason for experts to appreciate the integration of BIM into building management systems. Statistics speak louder than words: almost 30% fewer collisions, costs cut in half, 90% faster reporting on analytical data, with overall project cost savings reaching 50%. So what is BIM and why does it really pay to use it?
To come to the point, let’s dive deep into its main components. Building management stands on three pillars: BMS, FM, and BIM.
BMS means an automated Building Management System that has already been used by the owners of real estate, especially malls, hotels and business centers, as smart resource management helps them reduce building maintenance costs by 30%. BMS can detect certain situations inside a building and respond accordingly in line with prescribed algorithms by regulating temperature, ventilation, water supply, lighting, or turning systems on and off.
FM – Facility Management – is a concept to manage auxiliary indoor resources and processes that do not relate to the site’s primary function, like a ticket system that automatically generates maintenance and repair assignments. FM is primarily designed to:
- Save maintenance costs
- Ensure indoor process continuity
- Prevent emergency
Thanks to electronic document management based on FM, an owner and maintenance team can check consolidated statistics on all financial expenses: maintenance, repairs, property rental management, and service.
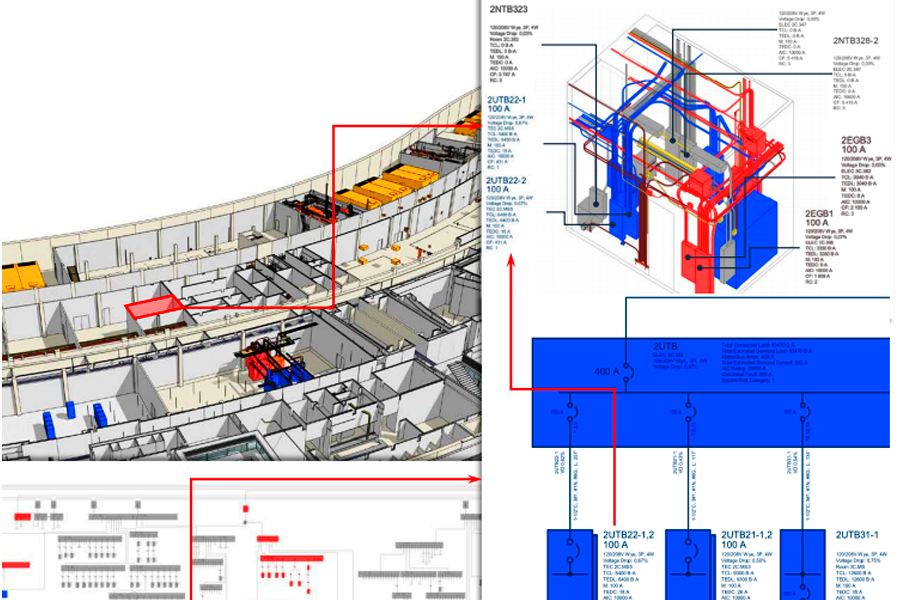
BIM – Building Information Modeling – is a technology to create an interactive and truly precise 3D model of a facility.
At the design stage, BIM streamlines both time management and drafting of construction cost estimate. Such a 3D model includes all engineering systems, and a change in one element automatically updates the entire model, including drawings, visualization, and work schedule.
Think of the opportunities that BIM offers in the long run! All three systems – BMS, FM and BIM – integrated via a smart app will make it possible to exchange data in real time (sensor readings, engineering systems’ status or failures). On the one hand, the application and the BMS are interconnected, and on the other, simulated scenarios are applied to process the building information model in a certain way.

Let’s take a closer look. For example, a clogged air filter alerts BMS, with the faulty unit being highlighted on the 3D model. An operator accurately locates the trouble and gets all the necessary information to fix it, like the model of faulty equipment, adjacent communications, etc. — something that helps drastically optimize both incidental expenses on eliminating emergency and labor efforts of administrative staff. This is particularly the case for operation of high-rise buildings or those with a complicated layout.
Preset scenario can concern any event requiring attention of security service: the current state of equipment (on / off), real-life sensor readings (temperature, pressure, etc.). A certain setting can display all these parameters on a BIM model, thus transforming this digital twin into an interactive model displaying real-life parameters of the facility systems.
If you need to repair equipment being in a hard-to-reach place or covered by engineering structures, a BIM model will show you its exact location, a particular spot to break through the wall or where to dismantle barriers.Thus, by combining BIM, BMS and FM into a single interactive building management model, real estate developers and property owners enjoy cost-effective maintenance and emergency mitigation, save vast sums of money and keep their nerves.